Have you ever wondered about the current population of capybaras? These fascinating creatures, known for their large size and sociable nature, have captured the curiosity of animal enthusiasts worldwide. In this article, we will explore the current status of capybaras and shed light on the estimated number of these unique rodents that remain in the wild. Join us on this captivating journey as we learn more about the population dynamics of capybaras and the efforts being made to ensure their conservation.

1. Habitat and Distribution
1.1 Natural Habitat
Capybaras, the largest rodents in the world, are native to South America. They are primarily found in semi-aquatic habitats such as rivers, swamps, marshes, and lakes. These water-loving creatures thrive in regions with abundant vegetation and easy access to water sources. The dense vegetation and water bodies provide the necessary cover and food for these herbivorous mammals.
1.2 Geographic Distribution
Capybaras have a widespread geographic distribution throughout South America. They can be found in various countries including Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, Colombia, and Peru, among others. The distribution of capybaras is particularly extensive in the Amazon rainforest, the Pantanal wetlands, and the Orinoco River basin. They are adapted to a range of environments from tropical rainforests to savannas, making them versatile in their habitat preferences.
2. Capybara Population Size
2.1 Historical Data of Capybara Population
Understanding the historical population trends of capybaras is crucial in assessing their current conservation status. Unfortunately, comprehensive historical data on capybara populations is limited. However, anecdotal evidence suggests that their numbers were much higher in the past. Due to a lack of systematic population surveys, it is challenging to estimate their historical population accurately.
2.2 Current Estimates of Capybara Population
Although exact figures are difficult to determine, current estimates suggest that capybara populations have experienced some fluctuations across their range. The most recent population assessments indicate that capybaras are generally abundant, particularly in areas with suitable habitat and minimal human disturbance. However, localized declines in some regions, largely due to human activities, have been observed.
3. Capybara Population Trends
3.1 Factors Affecting Capybara Population
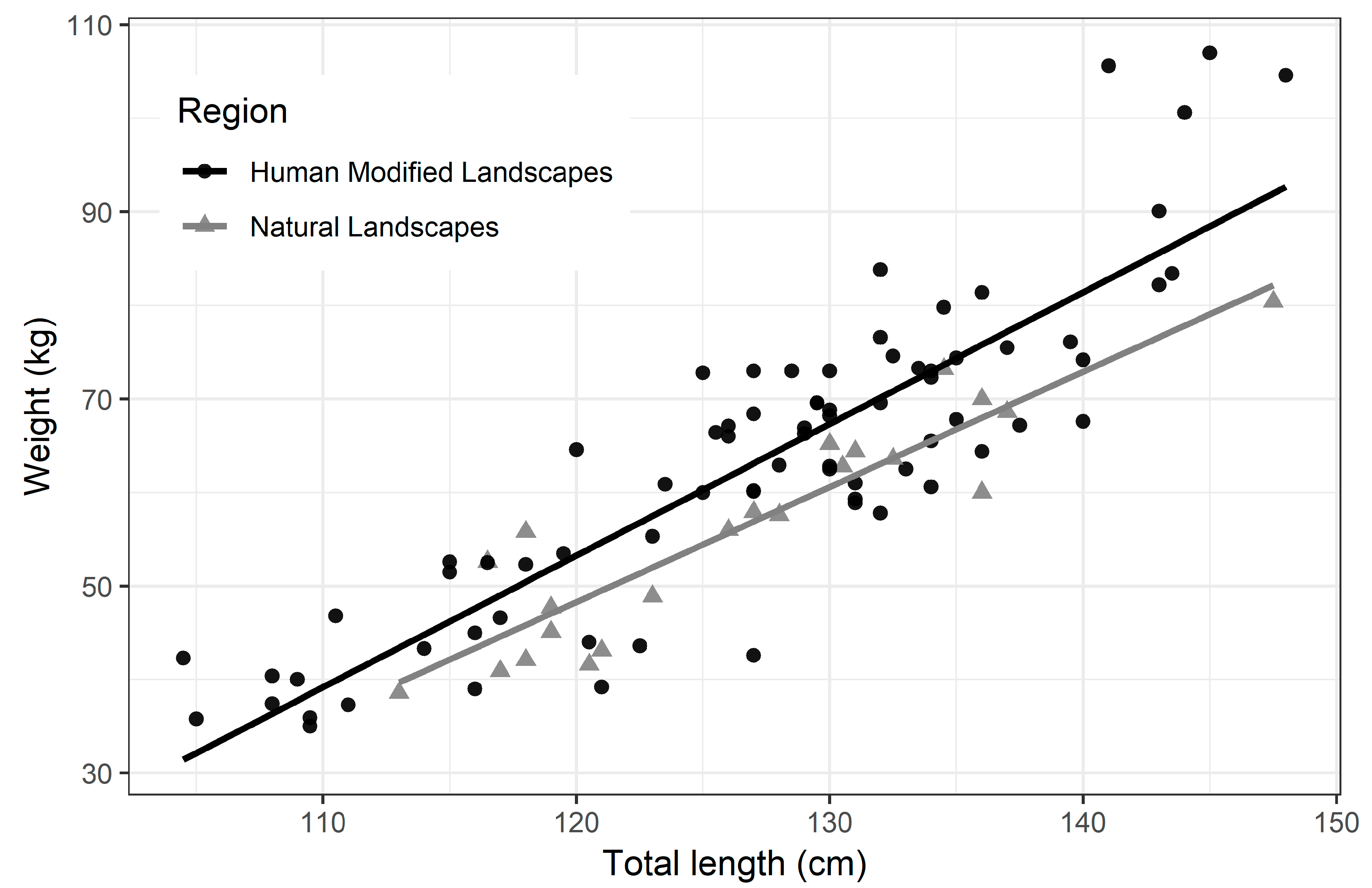
Several factors influence the population dynamics of capybaras. The availability of suitable habitat, access to water sources, and an abundance of food play critical roles in maintaining healthy population numbers. Additionally, predation, disease outbreaks, and climate fluctuations can impact their population size. Human activities such as habitat destruction, hunting, and encroachment also pose significant threats to capybara populations.
3.2 Population Growth or Decline
While capybara populations are generally stable across their range, localized declines have been observed due to human-induced factors. Habitat loss through deforestation and the conversion of wetlands for agriculture and infrastructure development are major drivers of population declines. Illegal hunting for their meat and fur, along with the capture of capybaras for the pet trade, also contribute to population reductions in certain areas.
4. Conservation Status
4.1 IUCN Red List Status
As per the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the capybara is categorized as a species of “Least Concern.” This designation implies that capybaras are not currently at risk of extinction at the global level. However, it is important to note that population trends and threats can vary across their range, warranting localized conservation efforts and monitoring.
4.2 Threats to Capybara Population
Despite their overall stable conservation status, capybaras face several threats that have the potential to impact their populations adversely. Habitat loss continues to be a significant threat, primarily driven by deforestation for agriculture and urbanization. Additionally, unregulated hunting, both for subsistence and commercial purposes, poses a serious concern, particularly in regions where capybara meat is valued and traded.

5. Monitoring and Research Efforts
5.1 Capybara Population Surveys
Efforts to monitor and understand capybara populations are vital for effective conservation strategies. Population surveys, utilizing various techniques such as camera traps, aerial surveys, and ground-based monitoring, are conducted to estimate population size, distribution, and demographic parameters. These surveys provide valuable insights into population trends, habitat requirements, and the effectiveness of conservation measures.
5.2 Research Studies and Initiatives
A significant amount of research is dedicated to studying capybara behavior, ecology, and population dynamics. Research initiatives focus on understanding their habitat preferences, reproductive biology, and movement patterns. These studies provide essential information for the development of robust conservation strategies that aim to mitigate threats and promote the long-term survival of capybaras.
6. Management and Conservation Measures
6.1 Captive Breeding Programs
Captive breeding programs play a crucial role in the management and conservation of capybaras. These programs ensure the genetic diversity of captive populations and can act as a potential source for reintroduction efforts. Additionally, captive breeding programs provide opportunities for public education and awareness regarding the importance of conserving these unique creatures.
6.2 Habitat Protection and Restoration
Preserving and restoring capybara habitats are essential for their long-term survival. Protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, contribute significantly to the conservation of capybaras by safeguarding their habitats from destructive human activities. Collaboration between local communities, governments, and conservation organizations is necessary to establish and implement effective habitat protection and restoration initiatives.
7. Importance of Capybara Population
7.1 Ecological Role
Capybaras play a vital ecological role as ecosystem engineers. Their grazing behavior helps maintain the balance of vegetation in wetland ecosystems, preventing the overgrowth of plants and promoting biodiversity. They also play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by consuming and dispersing seeds, aiding in the regeneration of plant communities. As a keystone species, the presence of capybaras positively influences the overall health and functioning of their habitats.
7.2 Socioeconomic and Cultural Significance
Capybaras hold significant socioeconomic and cultural value in certain regions. They are often actively hunted for their meat, which serves as a source of protein for local communities. Additionally, capybaras have cultural importance and may be featured in traditional ceremonies, folklore, and artistic expressions. Their existence contributes to the richness of cultural heritage and traditional practices in many South American communities.
8. Interaction with Humans
8.1 Conflict with Agriculture and Infrastructure
Capybaras occasionally come into conflict with human activities, particularly in areas where agriculture and infrastructure development overlap with their habitats. Capybaras can cause damage to crops and property, leading to conflicts with farmers and landowners. Balancing the needs of capybaras and human livelihoods requires careful planning, the implementation of appropriate mitigation measures, and the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices.
8.2 Coexistence Strategies
Developing coexistence strategies is crucial for minimizing conflicts between capybaras and humans. This involves raising awareness among local communities about the ecological importance of capybaras and implementing measures to reduce human-wildlife conflicts. Creating alternative food sources for capybaras, installing barriers to protect crops, and implementing integrated pest management techniques can contribute to peaceful coexistence between humans and capybaras.
9. Public Awareness and Education
9.1 Conservation Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are vital for garnering support and promoting the conservation of capybaras. These campaigns aim to educate the public about the ecological significance of capybaras, the threats they face, and the importance of conserving their habitats. Utilizing various communication channels such as social media, television, and community engagement programs, conservation campaigns play a critical role in fostering a collective responsibility for capybara conservation.
9.2 Educational Programs
Educational programs targeting schools, local communities, and tourists provide opportunities to educate people about capybaras and their conservation. These programs can include interactive workshops, guided tours, and educational materials that emphasize the importance of biodiversity conservation and sustainable practices. By fostering a sense of connection and understanding, these educational efforts contribute to the engagement and active participation of individuals in capybara conservation.
10. Future Prospects
10.1 Conservation Challenges
Despite their relatively stable population status, capybaras face ongoing conservation challenges. The continued loss and fragmentation of their habitats, along with the unsustainable hunting pressure, pose significant threats to their populations. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, communities, and conservation organizations to enforce stricter regulations, promote sustainable land-use practices, and increase protected areas effectively.
10.2 Potential Solutions
To ensure the future survival of capybaras, it is crucial to implement a combination of conservation measures. This includes strengthening habitat protection, restoring degraded ecosystems, and promoting sustainable use of natural resources. Additionally, implementing awareness campaigns, supporting scientific research, and fostering community involvement are essential for fostering a positive conservation outlook. By adopting multi-faceted approaches, we can safeguard the capybaras and their unique place in our world.
In conclusion, capybaras, with their charming nature and critical ecological role, are an invaluable part of South American ecosystems. While their overall population is deemed stable, localized declines and ongoing threats necessitate dedicated conservation efforts. By protecting their habitats, mitigating conflicts, and raising public awareness, we can secure a brighter future for these fascinating semi-aquatic creatures.